
Big Strategic Choices and Goals — 1.09
Markus Westerlund
Share this blog
The topic of the day is the big and tough choices of the business world. Strategic choices are the big choices in business. I like to use our strategy journey model as the base for every strategy.
How does one ignite a strategy? – By making three loops rotate simultaneously.
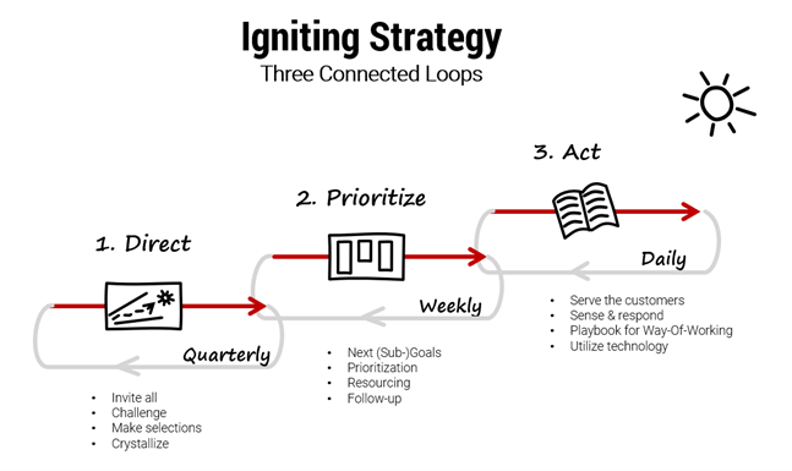
Let’s look at ‘We choose’ and ‘We crystallize’ phases of the first loop, in which we make the big decisions. How are these big decisions made?
Challenging current thinking

The whole concept of involving everyone and challenging the old models is covered in other blogs.
Analyzing the dangers and opportunities of trends helps to understand how one should react to them. Brutal reality means thinking about what the brutal reality is that we live in.
One must dare to dream. A great amount of thoughts form in the ‘Dreaming’ phase, but one also must dare to be paranoid. How could one ruin everything and save oneself from it? There comes a time when one must make tough decisions.
Summarizing everything on a single page
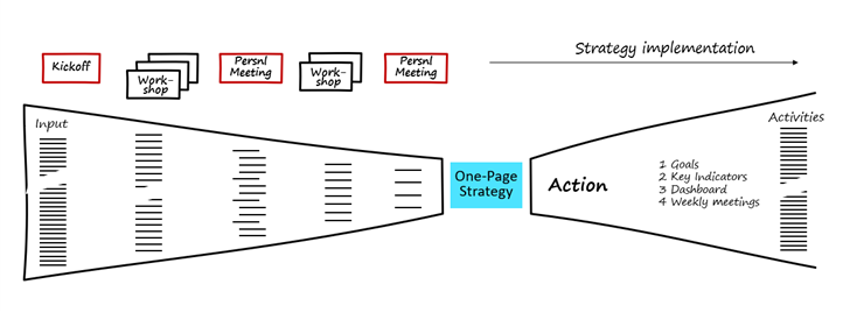
When we hold meetings with the whole staff, we get loads of comments. These comments are all documented using a digital board, for example, Trello. This is how we get everyone, including introverts, to write.
During the process, we got nearly four thousand comments. These comments are reduced to a bunch, and the tough decisions are the ones that remain. That is the point of the whole thing. In the end, we compress them all onto a Strategy 1Pager.
In the picture above you see a funnel, and that’s something that has to be in order. When you have a working funnel,
A.) You think of better ideas because everyone is involved in decision making,
B.) There is no separate implementation process because it happens automatically.
One time we were sitting with the board of a certain company, and someone made a comment:
“Those people don’t know how to think about the future, they’re so stuck in the present!”
That’s where they are wrong: There are many who think, and many who know-how. Because their thoughts are anchored in the present, their thought processes are usually of good quality.
Finding the big strategic choices
The hard part is finding the big decisions from the pile of comments. That is, in fact, the board’s job to say what the expectations are for this process.
What are the big questions that need to be answered? A group begins to figure these questions out and they produce answers. Once the process progresses, we come closer to the moment where the big and tough decisions make it through the filter.
I had a workshop with an organization, and the moment was very enjoyable when light was ignited in the people and the big choices were found. We also found an alternative way of thinking. Usually, when people in that organization think of the big things, they do it from a production perspective. We turned it into a customer-focused perspective. The group chair thought that this is a huge thing, and my response was “I know, right?”
Tough choices

Touch decisions can also be looked at one by one. Tough decisions are found by asking questions, and often it’s about the quality of these questions. One could ask what your company’s big business decision is. Now we are at the upper level and at the core of the business.
Whether we’re talking about a billion-dollar company or a micro-enterprise, they all have different businesses that are going through different phases in their lifecycle. The question is, are all these businesses where they belong — in their rightful home? Can we imagine having to get rid of a business so that the development budget would not be used in vain? We need to invest the money in the optimum spot, where we get the most feedback.
Business decisions
These big business decisions are truly massive. It is good to visualize the businesses by sorting them into a table that consists of four squares. That way it’s easier to see the horizon over the operation, the big picture, and decide whether it’s smart to invest in improving every business or should we make decisions about that business. That’s a conversation that easily skyrockets people to a satellite perspective.
In an earlier blog, I told the story about the five-day war in Kuwait and General Schwarzkopf. The general said, from the grassroots level you can easily make good decisions when the enemy attacks. However, if you’re looking at the situation from a satellite perspective, then you REALLY know what to do. – You need this perspective to see where your business lies.
Marketing choices
Another way of making tough decisions is through marketing decisions. This can also be thought of as geography: Where do we operate? If people who only work in Finland are asked, it can be that they haven’t even thought about working in another country. But, if a big growing company in Finland is finding it hard to find new potential, it can be natural to think about expanding their business abroad. Is it time to make marketing decisions? Is it time to evolve and expand? These questions will bring out big decisions.
People get anxious over worrying about having to make big analyses. In practice, the analysis doesn’t have to be a massive thing. It can be much simpler. You can start by making an initial assumption and ask yourself if you have already made a sufficient amount of background analysis? If you are not satisfied with what you have, you may need to do some more analysis? If even that is not enough you may need to start a full-fledged research project in order to achieve a satisfying conclusion to your analysis needs. The last option of course means you will have to reserve much more time and money and it may not fit your current schedule. In either case, at this stage of the process, you need to conclude if you have enough data from your analysis to make a high-quality conclusion?
The future is only guesses
The world-famous Swedish futurologist Kjell A. Nordström held an excellent presentation in Finland some years ago. He began his presentation with these words:
“The future cannot be studied, because it doesn’t exist.”
Whatever numbers we predict in the future are just guesses. Statistics and numbers can be looked back on and an estimate made based on their ascending or descending nature. All conclusions, however, are only guesses and beliefs. The person that knows the future does not exist.
I always say that the crystal balls that predict the future have been sold out and are no longer manufactured. But, it’s funny when you put a number in an Excel chart, it immediately becomes a fact in many people’s minds. That’s a clever way of pranking people, I tell you!
Hypotheses can indeed be made, and extra research is done if needed.
Customer choosing
The third way of making tough decisions is through customer choosing: We choose those who need to be our customers. We look at how we segment our customers into groups. How can we focus better on those customers that are very important to us and who need us?
Product selection
The fourth way is through product selection: We think about what it is we offer for different segments. With this way of thinking it’s possible to make very big decisions. Which products do we invest ourselves in? Which are most interesting to us? Which product development do we focus on?
Big opportunities and dangers
The fifth way is through big opportunities and dangers. In addition to the previous ones, I ask questions so that everyone’s thoughts focus on growth and avoiding overly great risks. It can be about digitizing, artificial intelligence, ecology, etc. Very big decisions can come out from these issues.
Hope
The last group on this list is quite exciting. What are the decisions that would awaken great hope in an organization? These decisions can give birth to an immense energy eruption and a sense of importance. Many technically thinking people can think that this is just utter nonsense. But nothing is as big of a decision as one that makes a hundred people run in the same direction, with excitement! One can make decisions while sitting in an ivory tower, but if you can’t make people implement them with excitement, nothing happens.
In conclusion, I can say that making the right decisions is very, very important! That’s what making tough decisions is all about.
Ignite your strategy! Read more.🔥
Recent Posts
Stradigo
Stradigo is a brand owned by Rdigo Oy (Business-ID: 2120844-1).
Learn more from our Imprint.
Rdigo Oy is registered in Finland as a Limited company. We are a strategy consultancy located in the Helsinki capital region.
We’ve been in business since 2007. The company name comes from the latin word Redigo, meaning both ‘I shape’ & ‘I renew’.
Stradigo combines the word strategy with Rdigo.